Rog Nidan evam Vikruti Vigyan
Leading the future of healthcare through excellence in medical education, research, and patient care.
Hospital Pathology Laboratory
Pathology Laboratory Services
- Clinical Pathology: Tests on blood, urine, and other bodily fluids to diagnose diseases.
- Cytology: Examines cells to diagnose diseases, such as cancer.
- Histopathology: Examines tissues to diagnose diseases

Haematology
Purpose:
Deals with blood samples to diagnose and treat blood related diseases.
Key Functions:
- Routine Examination: Analyzes complete blood cells and hemoglobin levels.
- Stained Blood Smear Studies: Identifies morphological abnormalities in blood cells and performs differential cell counts of white blood cells (leukocytes).
Overall, haematology labs play a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring blood-related diseases, aiding in appropriate medical treatment
Serology
Purpose:
Studies blood serum and other bodily fluids to detect and measure antibodies.
Key Functions:
- Diagnoses: Identifies infectious diseases by detecting specific antibodies in response to a pathogen.
- Monitors: Tracks the immune response to infections and vaccines.
Overall, serology labs play a crucial role in diagnosing infectious diseases, monitoring immune responses, and tracking the spread of diseases.
Histopathology Lab
Purpose:
Examines tissues to diagnose diseases by analyzing their microscopic structure.
Key Functions:
- Microscopic Examination: Analyzes the size, shape, and patterns of cells and tissues.
- Diagnosis: Identifies underlying pathologies and diseases.
Overall, histopathology labs play a crucial role in diagnosing diseases, guiding treatment decisions, and understanding the progression of diseases
Biochemistry
Purpose:
Analyzes biological samples like blood and urine to identify chemical components and detect abnormalities.
Key Functions:
- Diagnosis: Detects underlying pathologies and diseases.
- Monitoring: Tracks patient health and treatment effectiveness.
Overall, biochemistry labs play a vital role in diagnosing diseases, monitoring patient health, and guiding treatment decisions.
Microbiology Lab
Purpose:
Analyzes various biological samples to identify microorganisms causing infections and determine appropriate treatment.
Key Functions:
- Culture and Sensitivity Testing: Identifies microorganisms and determines their susceptibility to antibiotics.
- Serological & Immunological Tests: : Detects antibodies or antigens associated with specific infections.
- Surveillance: Monitors for potential outbreaks and helps implement infection control measures.
Overall, microbiology labs play a crucial role in diagnosing infectious
Services Offered
- Blood Tests: Complete Blood Count (CBC), Blood Chemistry.
- Urine Tests: Urinalysis, Urine Culture, and Urine Drug Screening.
- Stool Examination: Examines Culture to diagnose diseases.
- Cancer Screening: Pap smear.
- Infectious Disease Testing: Tests for bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.
- Sputum Examination: Sputum Culture and AFB test to diagnose diseases.
- Semen Examination: Semen Analysis.
Key Equipment and Technology
- Automated Analyzers: High-throughput analyzers for blood and urine tests.
- Microscopes: Light, and electron microscopes for tissue and cell examination.
- Laboratory Information System (LIS): Software for managing laboratory data and results.
Benefits
- Accurate Diagnosis: Pathology laboratory services provide accurate and reliable test results.
- Early Detection: Enables early detection of diseases, improving treatment outcomes.
- Personalized Medicine: Helps tailor treatment plans to individual patients.
- Disease Monitoring: Monitors disease progression and treatment response.
Quality Control and Assurance
- Quality Control: Laboratories implement quality control measures to ensure accurate and reliable results.
Hospital Pathology Laboratory
Pathology Laboratory Services
- Clinical Pathology: Tests on blood, urine, and other bodily fluids to diagnose diseases.
- Cytology: Examines cells to diagnose diseases, such as cancer.
- Histopathology: Examines tissues to diagnose diseases

Haematology
Purpose:
Deals with blood samples to diagnose and treat blood related diseases.
Key Functions:
- Routine Examination: Analyzes complete blood cells and hemoglobin levels.
- Stained Blood Smear Studies: Identifies morphological abnormalities in blood cells and performs differential cell counts of white blood cells (leukocytes).
Overall, haematology labs play a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring blood-related diseases, aiding in appropriate medical treatment
Serology
Purpose:
Studies blood serum and other bodily fluids to detect and measure antibodies.
Key Functions:
- Diagnoses: Identifies infectious diseases by detecting specific antibodies in response to a pathogen.
- Monitors: Tracks the immune response to infections and vaccines.
Overall, serology labs play a crucial role in diagnosing infectious diseases, monitoring immune responses, and tracking the spread of diseases.
Histopathology Lab
Purpose:
Examines tissues to diagnose diseases by analyzing their microscopic structure.
Key Functions:
- Microscopic Examination: Analyzes the size, shape, and patterns of cells and tissues.
- Diagnosis: Identifies underlying pathologies and diseases.
Overall, histopathology labs play a crucial role in diagnosing diseases, guiding treatment decisions, and understanding the progression of diseases
Biochemistry
Purpose:
Analyzes biological samples like blood and urine to identify chemical components and detect abnormalities.
Key Functions:
- Diagnosis: Detects underlying pathologies and diseases.
- Monitoring: Tracks patient health and treatment effectiveness.
Overall, biochemistry labs play a vital role in diagnosing diseases, monitoring patient health, and guiding treatment decisions.
Microbiology Lab
Purpose:
Analyzes various biological samples to identify microorganisms causing infections and determine appropriate treatment.
Key Functions:
- Culture and Sensitivity Testing: Identifies microorganisms and determines their susceptibility to antibiotics.
- Serological & Immunological Tests: : Detects antibodies or antigens associated with specific infections.
- Surveillance: Monitors for potential outbreaks and helps implement infection control measures.
Overall, microbiology labs play a crucial role in diagnosing infectious
Services Offered
- Blood Tests: Complete Blood Count (CBC), Blood Chemistry.
- Urine Tests: Urinalysis, Urine Culture, and Urine Drug Screening.
- Stool Examination: Examines Culture to diagnose diseases.
- Cancer Screening: Pap smear.
- Infectious Disease Testing: Tests for bacterial, viral, and fungal infections.
- Sputum Examination: Sputum Culture and AFB test to diagnose diseases.
- Semen Examination: Semen Analysis.
Key Equipment and Technology
- Automated Analyzers: High-throughput analyzers for blood and urine tests.
- Microscopes: Light, and electron microscopes for tissue and cell examination.
- Laboratory Information System (LIS): Software for managing laboratory data and results.
Benefits
- Accurate Diagnosis: Pathology laboratory services provide accurate and reliable test results.
- Early Detection: Enables early detection of diseases, improving treatment outcomes.
- Personalized Medicine: Helps tailor treatment plans to individual patients.
- Disease Monitoring: Monitors disease progression and treatment response.
Quality Control and Assurance
- Quality Control: Laboratories implement quality control measures to ensure accurate and reliable results.

Dr. Bhojraj Arun Chaudhari
M.D. PhD (Sch)
Assistant Prof. & HOD
Paper & Book Publication: View more

Dr. Nitant Vora
M.D.(Pathology)
Consulting Pathologist

Dr. Umesh Torgalli
DMRE.(Radiology)
Consulting Radiologist

Mrs. Aparna Zinjurde
Path Lab Technician

Mr. Mohandas Chilka
Radio X-Ray Technician

Dr. Nitant Vora
M.D.(Pathology)
Consulting Pathologist

Dr. Umesh Torgalli
DMRE.(Radiology)
Consulting Radiologist

Mrs. Aparna Zinjurde
Path Lab Technician

Mr. Mohandas Chilka
Radio X-Ray Technician
Department Gallery

Pathology Reporting Section
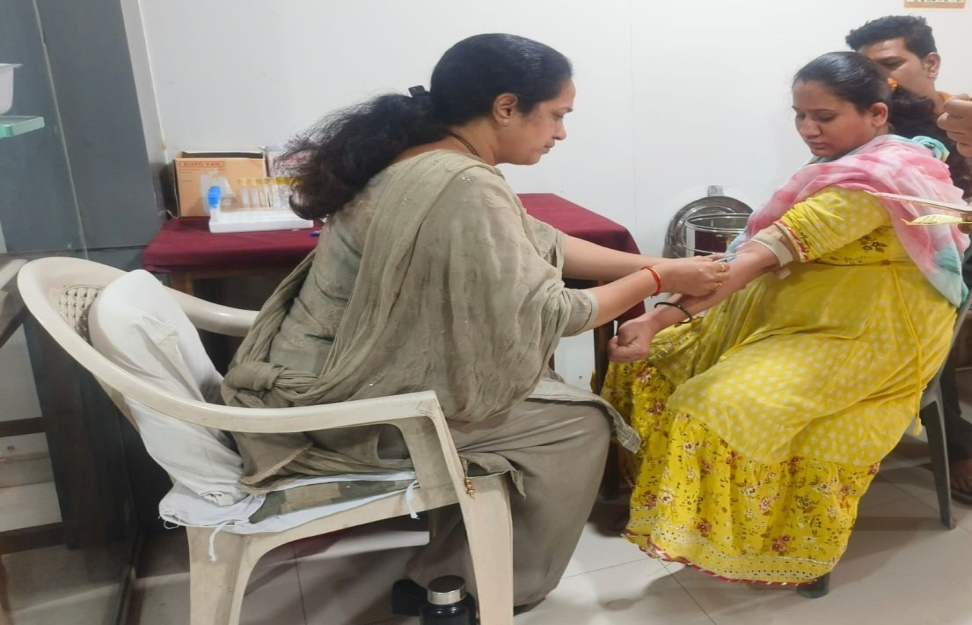

Pathology Sample Collection Section
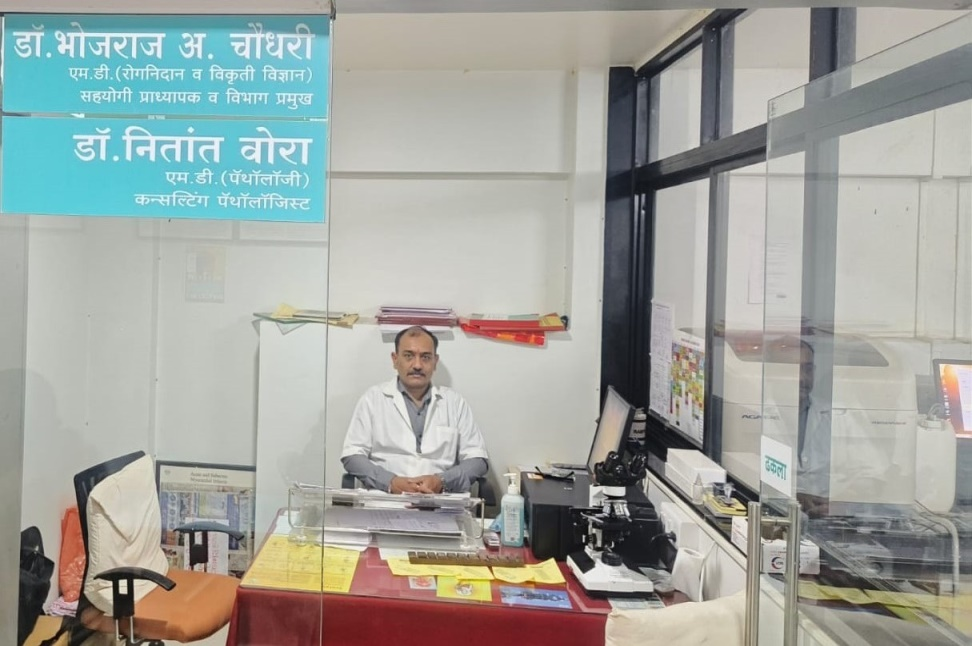

Pathology Head of Department Cabin
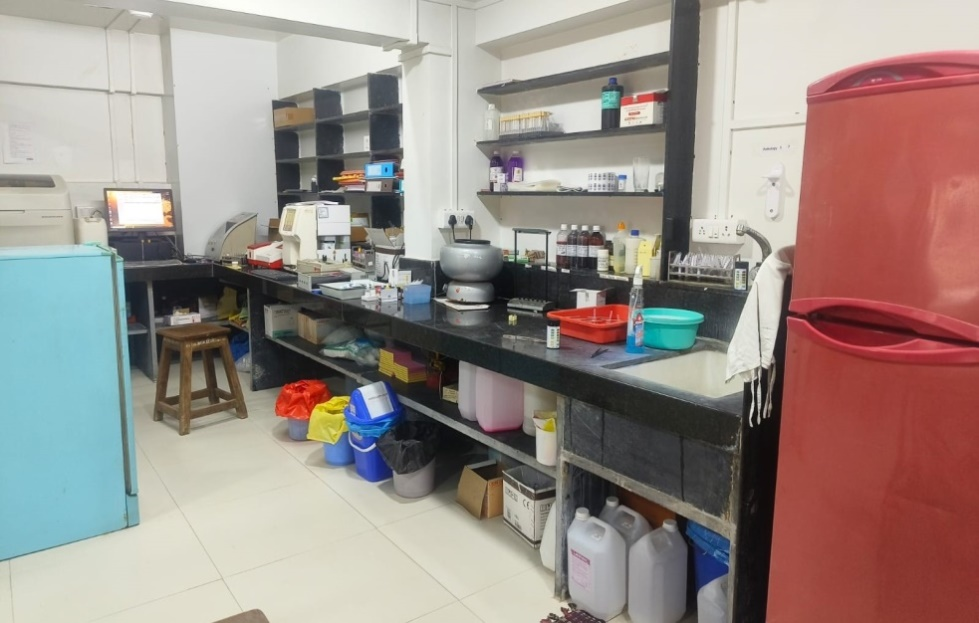

Pathology Internal Working Section
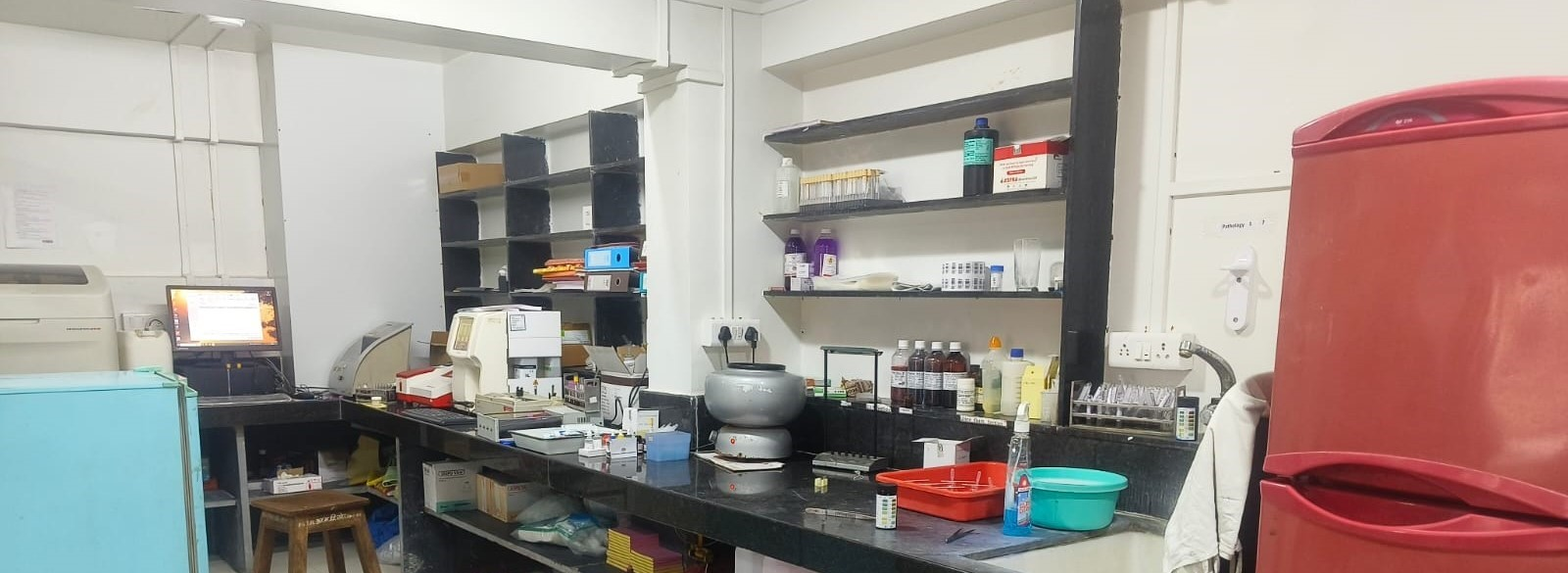

Pathology Internal area
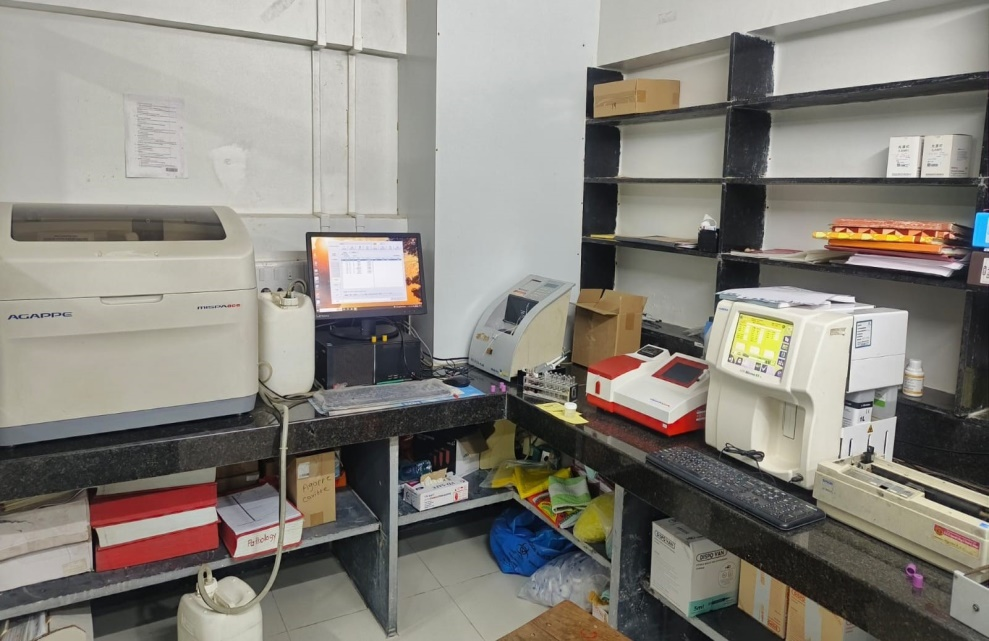

Pathology Machines Section
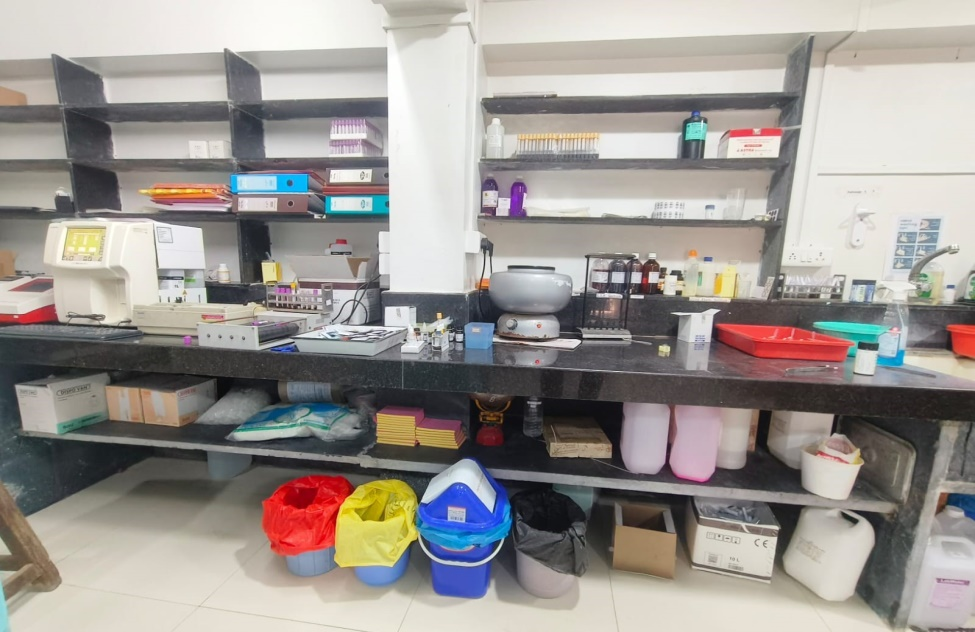

Pathology Internal area with BMW

Pathology Patients Waiting Section
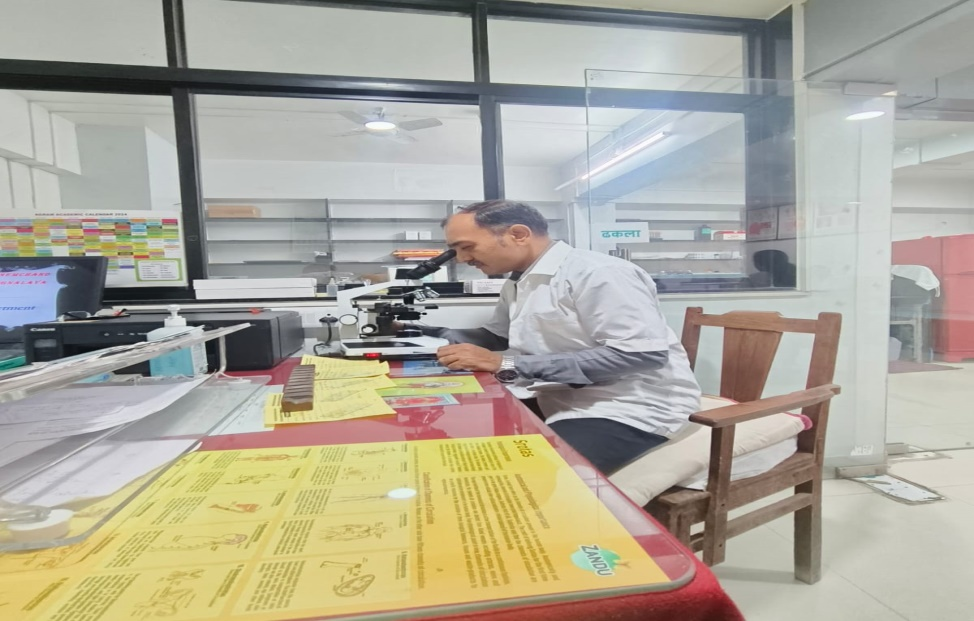

Pathology HOD Microscopic Exam Area
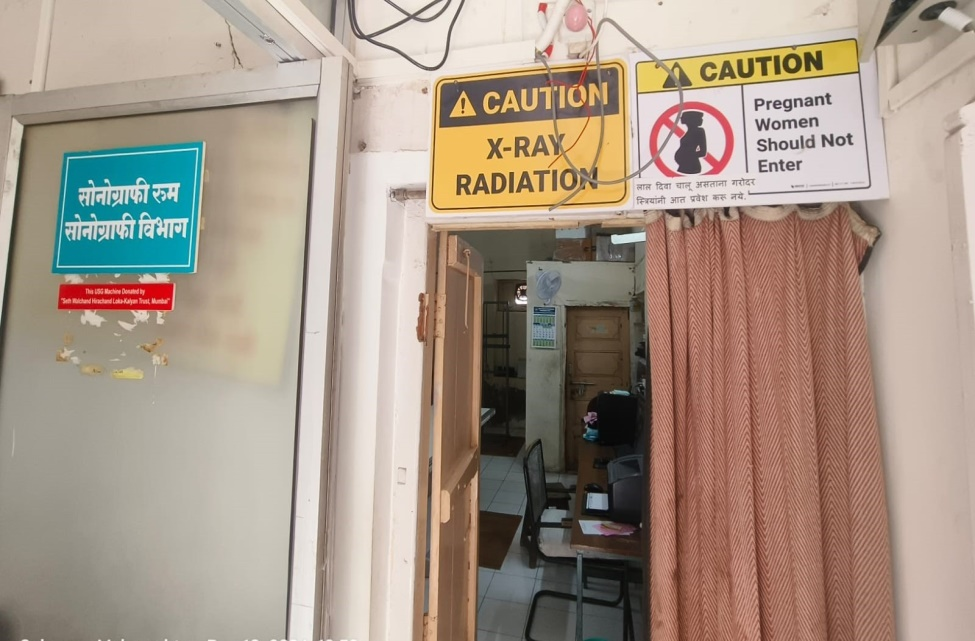

Radiology Department Entrance
Radiology Department Ultra Sonography
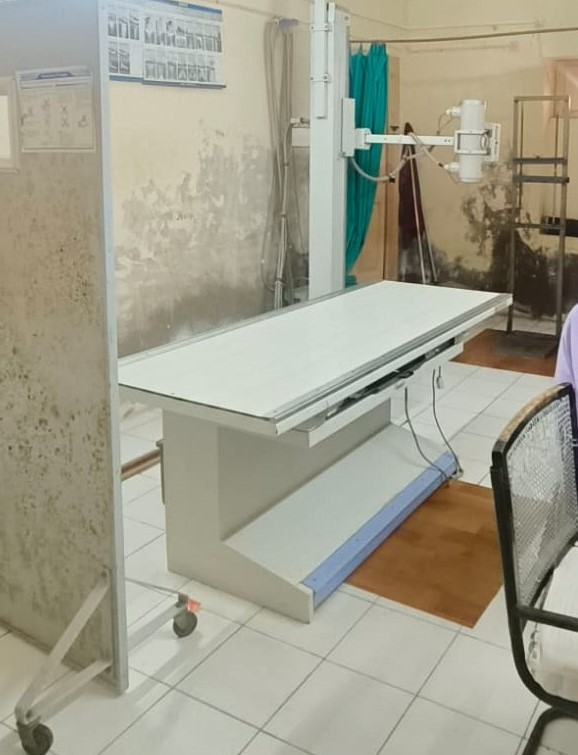

Radiology Department X-Ray Section
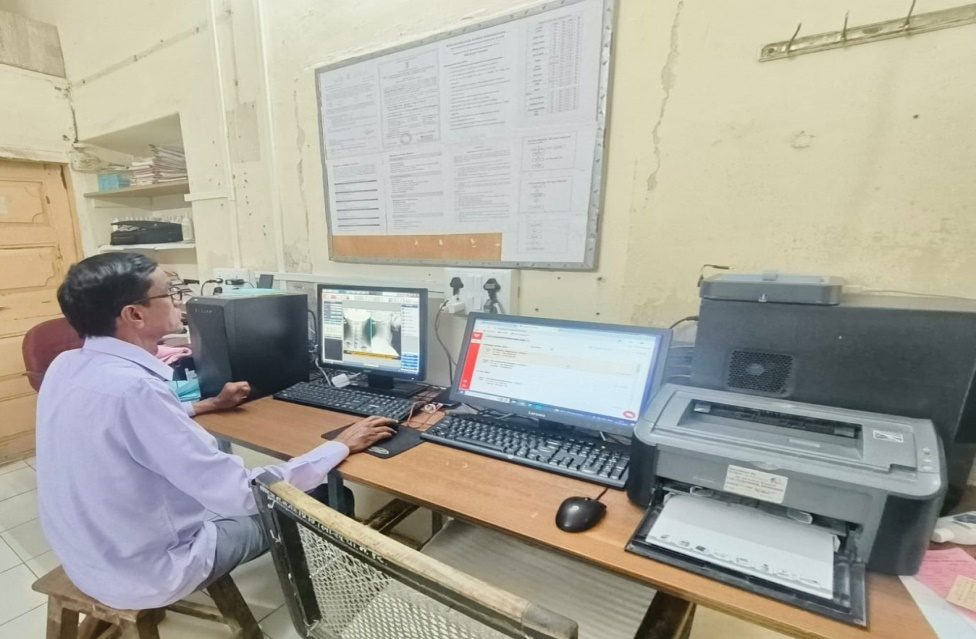

Radiology Department X-Ray/ USG Reporting

Radiology Ultra Sonography Rules Display



